It is becoming more and more routine to obtain an MRI scan if a thrower has a suspected injury to their UCL. But what does the MRI really tell us.
The UCL tears in different ways. We characterize the tear based on the tear location, the degree of tear, and if chronic features exist. A small slight stretch to the ligament does not show a tearing of the ligament on MRI. The MRI may show swelling around the ligament. A partial tear will show some fibers are disrupted and some are still intact. A full tear, just as implied, has no intact fibers. Also important is where the tear is located which can be either on the top end, the middle, or the bottom portion. Lastly, some tears happen with chronic changes to the ligament. Chronic refers to a process where the ligament has had prior small injuries that were able to heal but the ligament is changed compared to normal. For example, the ligament may become thickened or even have calcium deposits.
Why is this important? The tear characteristics can help determine the capacity of the ligament to heal without surgery. For example, partial tears at the top of the ligament heal much better without surgery compared to partial tears at the bottom of the ligament. Full tears at the bottom of the ligament have even less of a chance of healing.
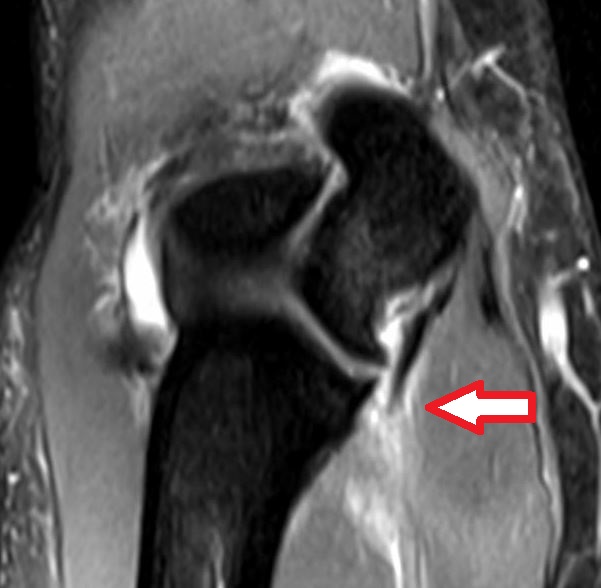
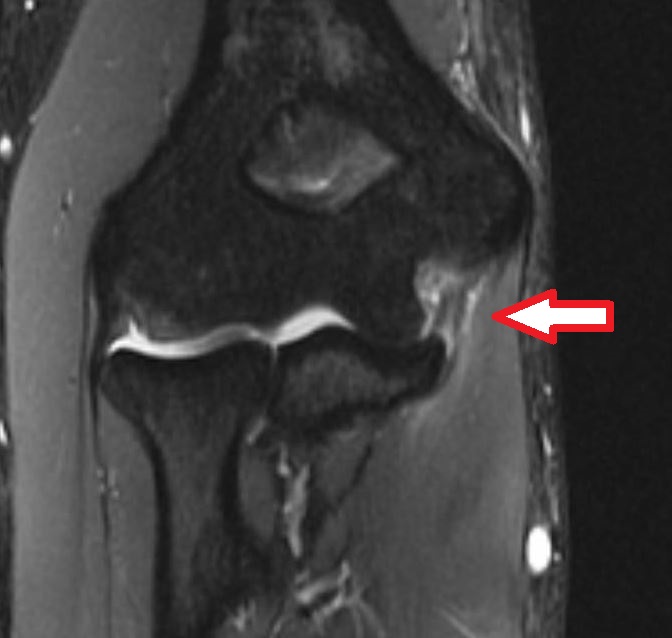
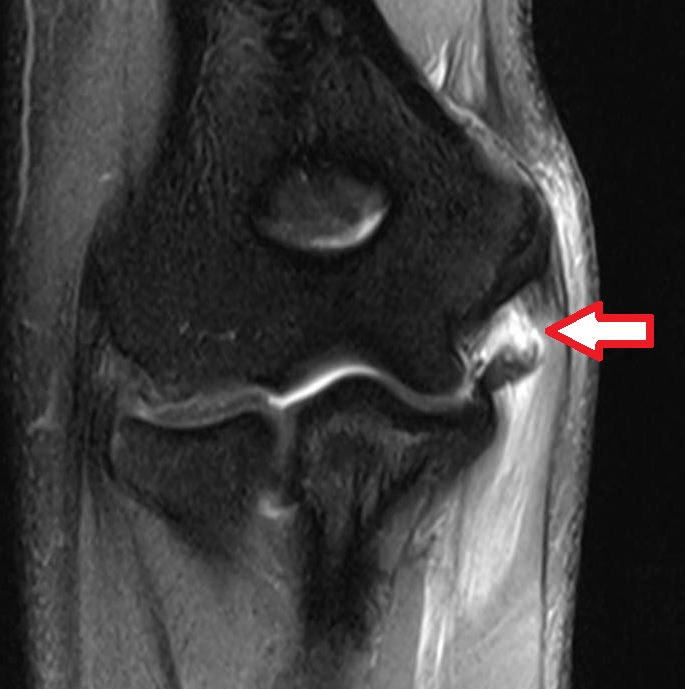
Figure 1. Shows a full ligament tear at the bottom insertion site onto the ulna bone.
Figure 2. Shows a partial tear in the mid substance of the ligament.
Figure 3. Shows a full tear at the top insertion site onto the humerus bone
It is amazing to think back to 1974 when Tommy John was diagnosed with a UCL tear by Dr. Frank Jobe before MRI was available.

